- Joined
- Dec 15, 2018
- Messages
- 74
- Reaction score
- 364
- Points
- 53
- Location
- Butler, PA
- Website
- www.pontiactransam.com
We know it's not a Trans Am, but it's still an important piece of Firebird history!
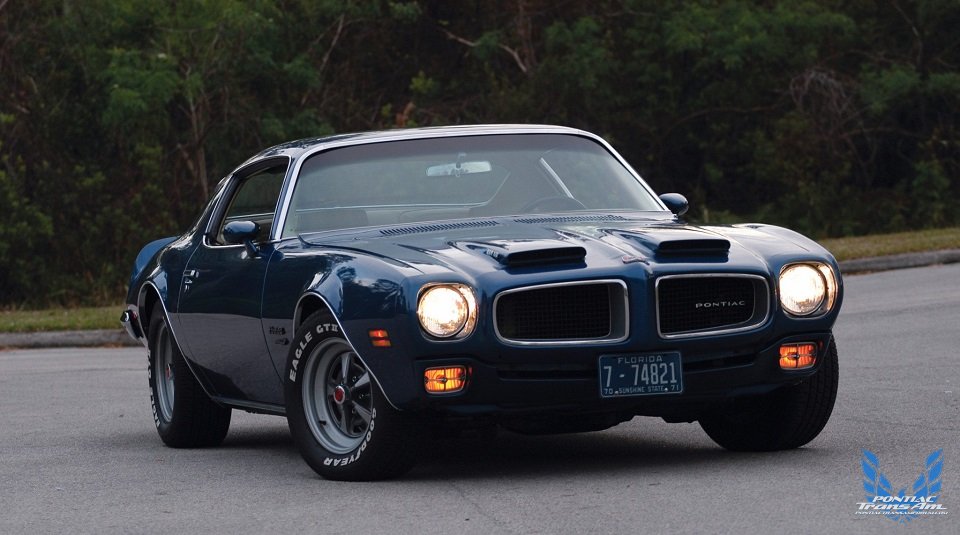

The story behind the development of GM’s F-body ponycars has been well documented. When Ford’s groundbreaking Mustang debuted in 1964, it tapped an emerging youth market that was hungry for a new type of car geared specifically to them. GM misjudged the public’s response to the Mustang and then scrambled to develop a similar style car after witnessing Ford’s unprecedented first model year sales success. Chevrolet was the lead division in engineering the F-body, and Pontiac grudgingly accepted the platform for their use in March 1966, only after GM management turned down PMD General Manager John DeLorean’s proposal for his own Mustang fighter.
Pontiac didn’t have much time to transform the Firebird from its Camaro configuration before releasing it in February 1967. Their design and engineering lead time was significantly reduced and consequently, the Firebird was forced to use quite a bit of Camaro sheetmetal and other components. Competition between Pontiac and Chevrolet was intense, and having to use the other division’s engineering and design was a bitter pill for DeLorean’s maverick staff to swallow.
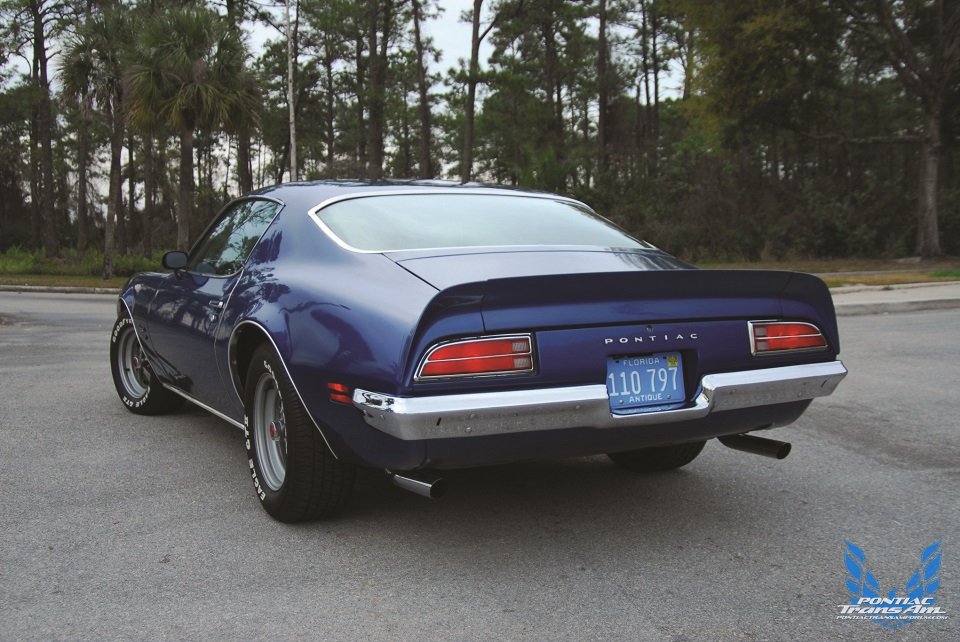

The circumstances surrounding the second generation Firebird were another story. Pontiac actually began working on their second generation just as the first Firebirds were hitting dealer showrooms. From design to engineering, Pontiac dominated the divisional rivalry, and this time around the Firebird would be all Pontiac from roof to road. There was little carried over to the second generation with the exception of the Trans Am nameplate and basic engine configurations. The suspension was tuned for more responsive handling with little compromise to ride comfort. Computer aided engineering chose the proper front and rear spring deflection rates predicated on model and usage. Stabilizer bars were used front and rear and the steering box was mounted ahead of the front axle for better response.
The sexy new body was rooted in GM styling chief Bill Mitchell’s infatuation with Italian sports car design. GM chose heavily from the rounded shapes of Ferrari and Maserati, and it showed in the smooth flow of fender lines, the curved window glass and raked windshield. One remarkable difference from pervious GM designs was the lack of a quarter window. Instead, the doors were lengthened to take up a larger portion of the quarter. The massive doors were heavy, however the side appearance was cleaner and far sportier. A lift bar door handle added to the smooth side look. Chrome was distinctively absent. The Native American-inspired Firebird emblem was on the decklid and the nose of all but base model cars.
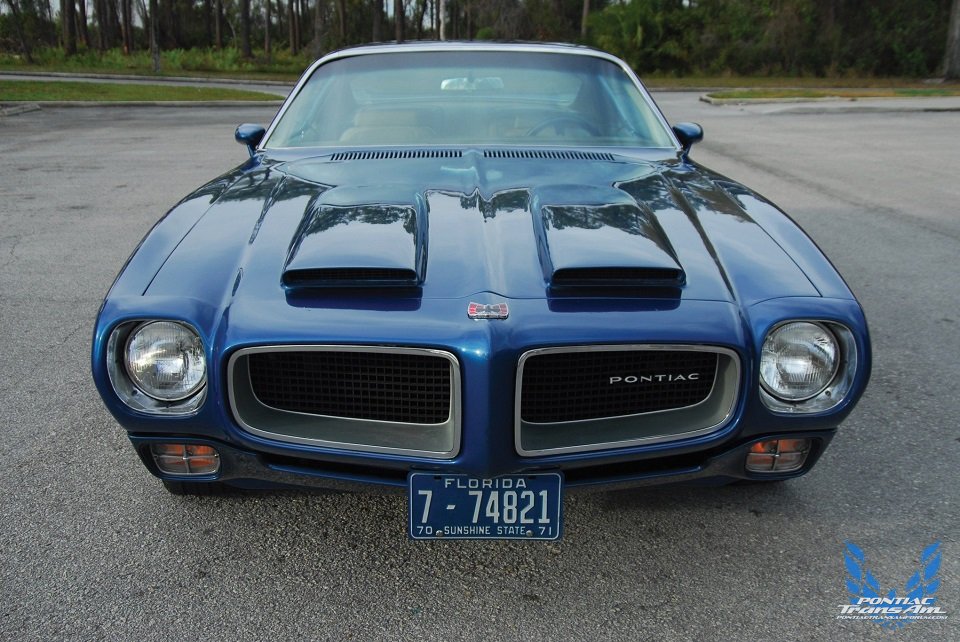

Up front, the twin nostril grille and single headlamps provided a clean appearance, thanks to the use of Endura to create a bumper-less front end with a valance that cleanly rolled beneath the grille with large cross hair parking lamps mounted in the lower corners of the valance. At the rear, the smooth tumble home enhanced the Firebirds fuselage shape. The tail was flat and filled with twin tail lamps that met the quarter panel’s round rear profile. A recessed tag housing, thin blade chrome rear bumper, and rounded lower valance completed the rear end’s clean look.
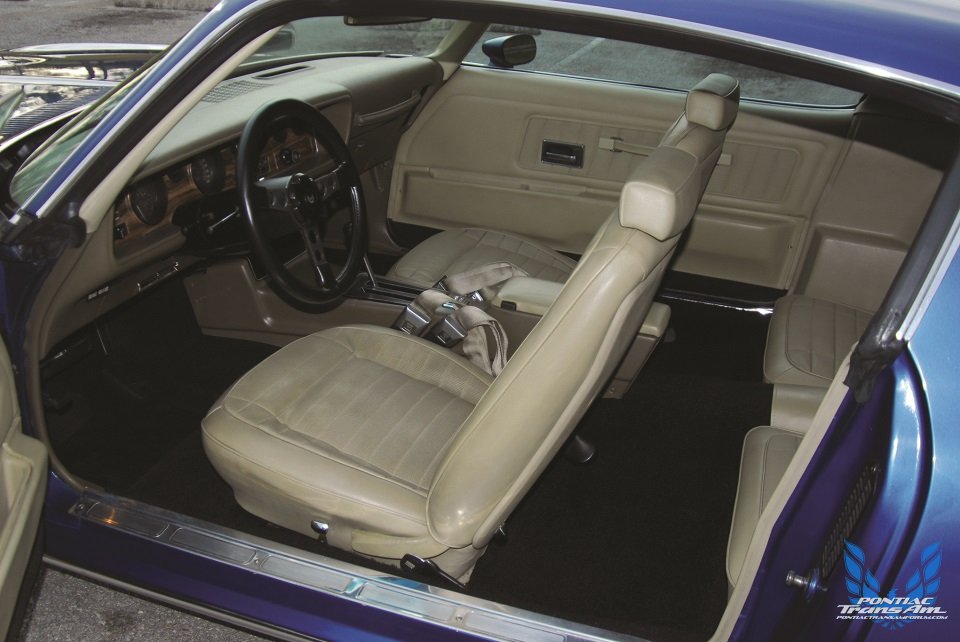
Inside, the Firebird’s wide, expansive dash housed the instrument panel consisting of three center nacelles for gauges, with smaller gauges at the right and room for the heater controls and additional switches and knobs. Directly below the center of the dash was another stack that contained the radio and ashtray. Even the base interior was sumptuous, with Pontiac’s indestructible Morrokide vinyl upholstery covering the bucket seats and door panels. The quarter trim panels and headliner were composed of molded polymeric material that provided a smooth surface and absorbed sound.

The 1970 Pontiac line up was composed of the base Firebird with 250 cid six, the mid range, 350 cid Espirit, the 400 cid Formula 400, and the 400 cid Ram Air Trans Am. Of the four, perhaps the most intriguing was the Formula 400. While the Trans Am was loaded with visuals like a shaker hood, fender mounted air extractors, wild front air spoiler, rear wheel opening air spoilers, and wide center stripe, the Formula had none of these. For those who preferred to have a muscular pony car sans the exterior adornments, the Formula 400 was just the ticket. Outside, the only difference between the mild mannered Espirit and the Formula was a special fiberglass hood that sported a pair of front reaching hood scoops (first considered for the Trans Am), sport style dual outside mirrors, and a pair of Formula 400 scripts below the Firebird nameplate on the fenders.
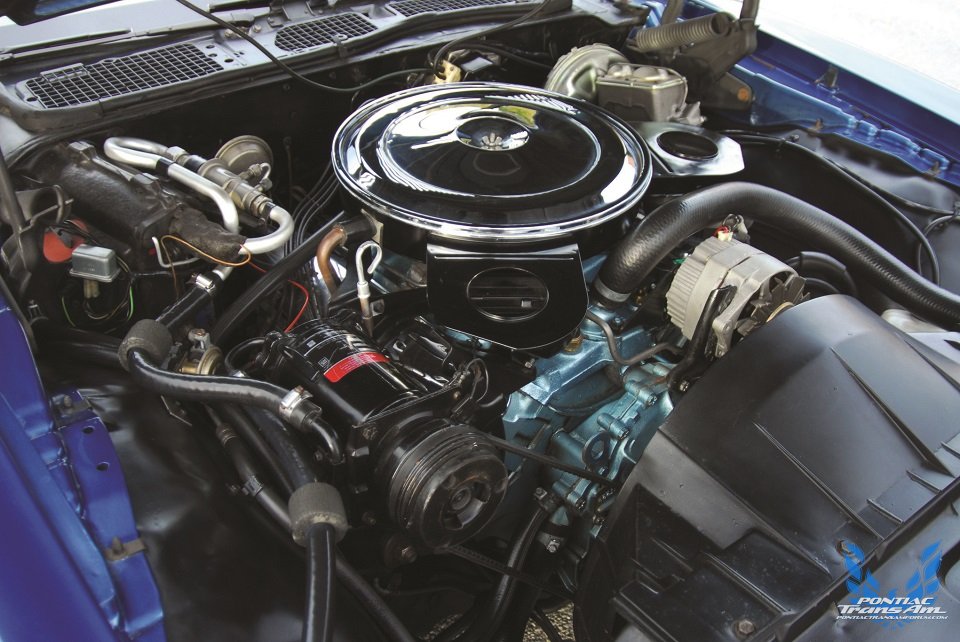

Under the sheetmetal, however, is where the $3,440 Formula’s credentials lay. Standard engine was the 400 cid V8 which generated 330 horsepower @ 4800rpm and 430 lbs.-ft. torque @ 3000rpm. Car & Driver tested a Formula 400 with this engine and automatic transmission and recorded a 0-60 acceleration time of 6.4 seconds and quarter mile performance of 14.7 seconds at 98.9mph.
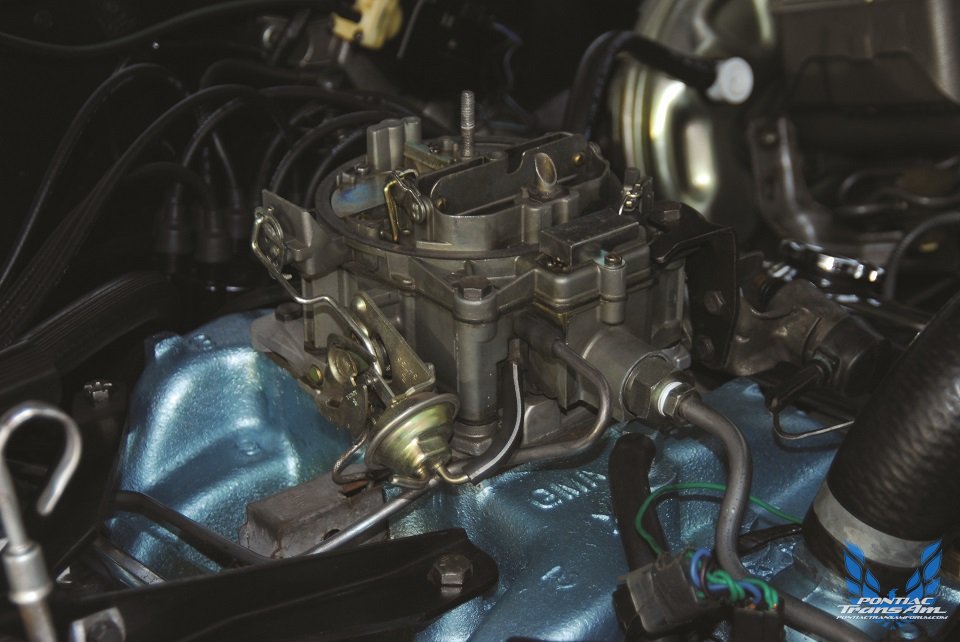
The optional engine was the Ram Air III V8, which produced 345 horsepower @ 5000rpm and 430 lbs.-ft. torque @ 3400rpm, thanks in part to a higher compression and a more aggressive camshaft profile. While Pontiac offered a 370 horsepower Ram Air IV, it never found its way into a Formula 400. On the Ram Air III equipped Formulas, the hood scoops were opened and a pair of rubber “boots” were fitted to the hood’s underside. They snugged up to holes in the air cleaner snorkels and fed cold outside air to the Rochester Quadra Jet carburetor. Subtle “RAM AIR” decals were affixed to the outboard sides of the hood scoops. The Formula’s 400 engine was dressed up with chromed air cleaner lid and valve covers. Dual exhausts with chrome tips were also standard.
Standard transmission was the M13, a heavy duty Dearborn three-speed manual box. A pair of Muncie four speeds was offered optionally, the wide ratio M20 and close ratio M21. Also optional was the M40 three-speed Turbo Hydra Matic transmission. A 3.55:1 rear axle ratio was standard, while air conditioned models received 3.31:1 ratios. Optional ratios were 3.07:1 and 3.73:1.

The Formula received a firmer suspension with 300-pounds/inch deflection in the front springs and 103 pounds/inch in the rear. The front stabilizer measured 1.125 inches in the front and the rear bar was .620 inches with firm control shocks mounted at all four corners. Front disc brakes were standard with rear drums. Standard tires were F70 x 14 on six-inch steel rims. The Trans Am’s tighter suspension was offered optionally. It consisted of 300 pounds/inch front and 126 pounds/inch springs in the rear, 1.250 inch stabilizer bar at the front, and fat .875 inch bar aft. Wider F60x 15 Polyglas tires mounted on 15 x 7 Rally II wheels without trim rings rounded out the package. Add the variable ratio power steering and power brakes and the Formula responded right now! to steering input and could dive deeper into corners and come out faster. Its only competition was big brother Trans Am and the Corvette.

Inside, the Formula’s instrument panel was faced in a wood grained appliqué. Optional was a Rally Gauge that placed an 8000-rpm tach in the left housing along with a small analog clock. In the smaller center housing was the engine temperature and oil pressure gauges. The right housing contained the 160mph speedometer with the smaller fuel gauge and voltmeter to the far right. Two consoles were offered, one between the front buckets that contained the transmission shifter, the other between the optional rear buckets.

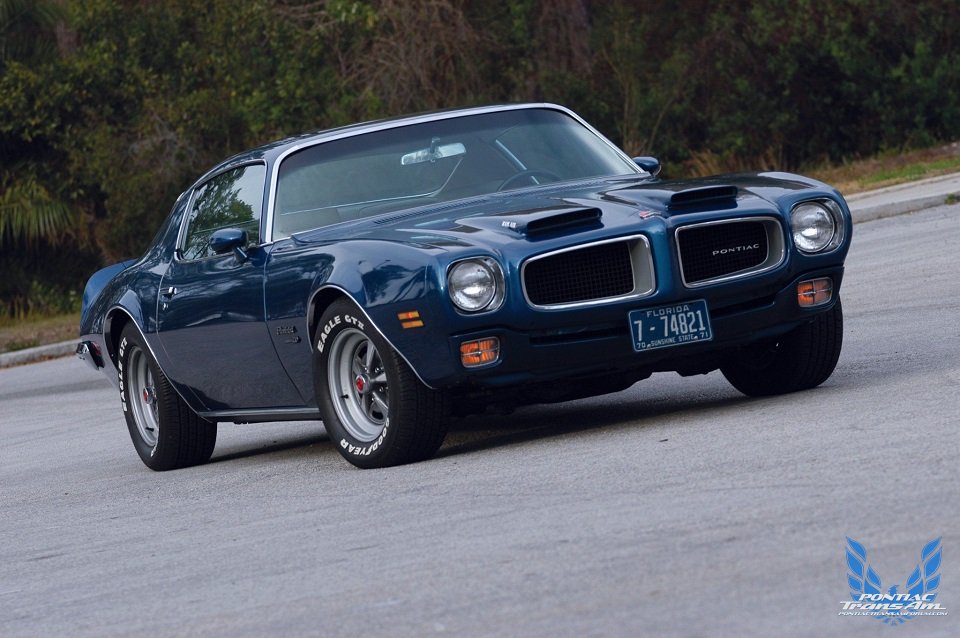
Of the 7,708 Formula 400s produced in 1970, 2,777 were equipped with manual transmissions. Exactly 4,931 were fitted with the M40 automatic transmission. One of those M40 equipped Formulas is owned by Jack Nichols of Orlando, Fla. Jack performed a complete restoration on the Formula several years ago, bringing it back to correct factory standards. The Atoll Blue Formula is fitted with the optional Ram Air engine, open scoops and underhood induction system. Inside, the tan Morrokide interior features console, optional three-spoke Formula steering wheel with padded rim, Rally gauges and air conditioning.
Courtesy of Heacock Classic

The story behind the development of GM’s F-body ponycars has been well documented. When Ford’s groundbreaking Mustang debuted in 1964, it tapped an emerging youth market that was hungry for a new type of car geared specifically to them. GM misjudged the public’s response to the Mustang and then scrambled to develop a similar style car after witnessing Ford’s unprecedented first model year sales success. Chevrolet was the lead division in engineering the F-body, and Pontiac grudgingly accepted the platform for their use in March 1966, only after GM management turned down PMD General Manager John DeLorean’s proposal for his own Mustang fighter.
Pontiac didn’t have much time to transform the Firebird from its Camaro configuration before releasing it in February 1967. Their design and engineering lead time was significantly reduced and consequently, the Firebird was forced to use quite a bit of Camaro sheetmetal and other components. Competition between Pontiac and Chevrolet was intense, and having to use the other division’s engineering and design was a bitter pill for DeLorean’s maverick staff to swallow.

The circumstances surrounding the second generation Firebird were another story. Pontiac actually began working on their second generation just as the first Firebirds were hitting dealer showrooms. From design to engineering, Pontiac dominated the divisional rivalry, and this time around the Firebird would be all Pontiac from roof to road. There was little carried over to the second generation with the exception of the Trans Am nameplate and basic engine configurations. The suspension was tuned for more responsive handling with little compromise to ride comfort. Computer aided engineering chose the proper front and rear spring deflection rates predicated on model and usage. Stabilizer bars were used front and rear and the steering box was mounted ahead of the front axle for better response.
The sexy new body was rooted in GM styling chief Bill Mitchell’s infatuation with Italian sports car design. GM chose heavily from the rounded shapes of Ferrari and Maserati, and it showed in the smooth flow of fender lines, the curved window glass and raked windshield. One remarkable difference from pervious GM designs was the lack of a quarter window. Instead, the doors were lengthened to take up a larger portion of the quarter. The massive doors were heavy, however the side appearance was cleaner and far sportier. A lift bar door handle added to the smooth side look. Chrome was distinctively absent. The Native American-inspired Firebird emblem was on the decklid and the nose of all but base model cars.

Up front, the twin nostril grille and single headlamps provided a clean appearance, thanks to the use of Endura to create a bumper-less front end with a valance that cleanly rolled beneath the grille with large cross hair parking lamps mounted in the lower corners of the valance. At the rear, the smooth tumble home enhanced the Firebirds fuselage shape. The tail was flat and filled with twin tail lamps that met the quarter panel’s round rear profile. A recessed tag housing, thin blade chrome rear bumper, and rounded lower valance completed the rear end’s clean look.
Inside, the Firebird’s wide, expansive dash housed the instrument panel consisting of three center nacelles for gauges, with smaller gauges at the right and room for the heater controls and additional switches and knobs. Directly below the center of the dash was another stack that contained the radio and ashtray. Even the base interior was sumptuous, with Pontiac’s indestructible Morrokide vinyl upholstery covering the bucket seats and door panels. The quarter trim panels and headliner were composed of molded polymeric material that provided a smooth surface and absorbed sound.

The 1970 Pontiac line up was composed of the base Firebird with 250 cid six, the mid range, 350 cid Espirit, the 400 cid Formula 400, and the 400 cid Ram Air Trans Am. Of the four, perhaps the most intriguing was the Formula 400. While the Trans Am was loaded with visuals like a shaker hood, fender mounted air extractors, wild front air spoiler, rear wheel opening air spoilers, and wide center stripe, the Formula had none of these. For those who preferred to have a muscular pony car sans the exterior adornments, the Formula 400 was just the ticket. Outside, the only difference between the mild mannered Espirit and the Formula was a special fiberglass hood that sported a pair of front reaching hood scoops (first considered for the Trans Am), sport style dual outside mirrors, and a pair of Formula 400 scripts below the Firebird nameplate on the fenders.

Under the sheetmetal, however, is where the $3,440 Formula’s credentials lay. Standard engine was the 400 cid V8 which generated 330 horsepower @ 4800rpm and 430 lbs.-ft. torque @ 3000rpm. Car & Driver tested a Formula 400 with this engine and automatic transmission and recorded a 0-60 acceleration time of 6.4 seconds and quarter mile performance of 14.7 seconds at 98.9mph.

The optional engine was the Ram Air III V8, which produced 345 horsepower @ 5000rpm and 430 lbs.-ft. torque @ 3400rpm, thanks in part to a higher compression and a more aggressive camshaft profile. While Pontiac offered a 370 horsepower Ram Air IV, it never found its way into a Formula 400. On the Ram Air III equipped Formulas, the hood scoops were opened and a pair of rubber “boots” were fitted to the hood’s underside. They snugged up to holes in the air cleaner snorkels and fed cold outside air to the Rochester Quadra Jet carburetor. Subtle “RAM AIR” decals were affixed to the outboard sides of the hood scoops. The Formula’s 400 engine was dressed up with chromed air cleaner lid and valve covers. Dual exhausts with chrome tips were also standard.
Standard transmission was the M13, a heavy duty Dearborn three-speed manual box. A pair of Muncie four speeds was offered optionally, the wide ratio M20 and close ratio M21. Also optional was the M40 three-speed Turbo Hydra Matic transmission. A 3.55:1 rear axle ratio was standard, while air conditioned models received 3.31:1 ratios. Optional ratios were 3.07:1 and 3.73:1.

The Formula received a firmer suspension with 300-pounds/inch deflection in the front springs and 103 pounds/inch in the rear. The front stabilizer measured 1.125 inches in the front and the rear bar was .620 inches with firm control shocks mounted at all four corners. Front disc brakes were standard with rear drums. Standard tires were F70 x 14 on six-inch steel rims. The Trans Am’s tighter suspension was offered optionally. It consisted of 300 pounds/inch front and 126 pounds/inch springs in the rear, 1.250 inch stabilizer bar at the front, and fat .875 inch bar aft. Wider F60x 15 Polyglas tires mounted on 15 x 7 Rally II wheels without trim rings rounded out the package. Add the variable ratio power steering and power brakes and the Formula responded right now! to steering input and could dive deeper into corners and come out faster. Its only competition was big brother Trans Am and the Corvette.

Inside, the Formula’s instrument panel was faced in a wood grained appliqué. Optional was a Rally Gauge that placed an 8000-rpm tach in the left housing along with a small analog clock. In the smaller center housing was the engine temperature and oil pressure gauges. The right housing contained the 160mph speedometer with the smaller fuel gauge and voltmeter to the far right. Two consoles were offered, one between the front buckets that contained the transmission shifter, the other between the optional rear buckets.

Of the 7,708 Formula 400s produced in 1970, 2,777 were equipped with manual transmissions. Exactly 4,931 were fitted with the M40 automatic transmission. One of those M40 equipped Formulas is owned by Jack Nichols of Orlando, Fla. Jack performed a complete restoration on the Formula several years ago, bringing it back to correct factory standards. The Atoll Blue Formula is fitted with the optional Ram Air engine, open scoops and underhood induction system. Inside, the tan Morrokide interior features console, optional three-spoke Formula steering wheel with padded rim, Rally gauges and air conditioning.
Courtesy of Heacock Classic

